Internet Protocol
The IP (Internet Protocol) is the process by which information is transported from one computer to some other computer on the web. All computer (called a host) on the web has at minimal of one IP address that distinguishes it from all other pc on the web.
Information on a web Protocol network is configured into packages. Every IP address includes header (defines Identification, type of service, destination, and other info) and the message information itself.
The following diagram shows the IP header format which is of 20 octets length.
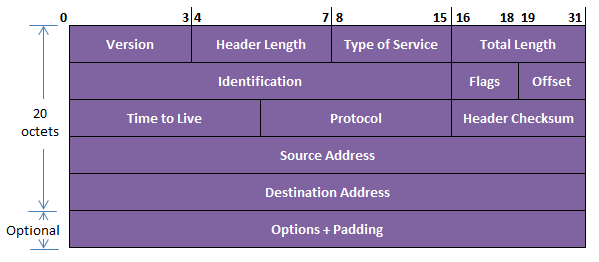
1. Version
This field specifies the version of the protocol used in it.
2. Header length
Specifies the number of 32 bit words present in the header. It is 5 for 20 octet’s header.
3. Type of service
This field provides guidance about the relative priority to be given to a packet by the IP module present in the end system and Router.
4. Total length
Specifies the total length of the IP datagram including the header in the terms of octets.
5. Identification
Contains a unique 16 bit number to identify the datagram.
6. Flags
It is in 3 hit fields that can be used to specify whether it is that last fragment in the original packet or whether fragmentation is required or not.
7. Offers
Gives the distance from the beginning where the fragment resides within the datagram.
8. Time to live
Contains a value in seconds that specifies how long the data gram is valid in the internet. Each time it passes through a Router; the value is decremented by one. When this value reaches 0, the datagram is no longer valid.
9. Protocol
Indicates which higher level protocol should receive the packet at the destination.
10. Header check sum
Used for error detection.
11. Source address
Specifies the IP address of the sender.
12. Destination address
Specifies the IP address of the destination.
Average Acceleration Calculator
Average acceleration is the object's change in speed for a specific given time period. ...
When an object falls into the ground due to planet's own gravitational force is known a...
In Mathematics, the permutation can be explained as the arrangement of objects in a particular order. It is an ordered...
A rectangle can be explained as a 4-sided quadrilateral which contains equal opposite sides. In a rectangle
A three sided polygon which has three vertices and three angles is called a triangle. Equilateral triangle...






